Am I at risk for colorectal cancer?
Yes, everyone is at risk for colon cancer. Colorectal cancer occurs most often in men and women age 45 and older. HOWEVER, people born after 1990 have TWICE the risk of colon cancer, and FOUR TIMES the risk of rectal cancer. People with a family history of colorectal cancer or colon polyps should start screening with colonoscopy at age 40 or 10 years sooner than their affected relative. This is CRITICAL!
Timely screenings save lives. Colorectal cancer usually starts from polyps in the colon or rectum. Screening finds polyps so that they can be removed before they turn into cancer. Screening tests also find colorectal cancer early, when it is most treatable. Both colon polyps and early colon cancer DO NOT HAVE SYMPTOMS, so getting screened is the way to prevent and detect early.
How common is IT?
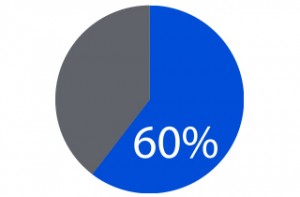 Colon cancer is the 2nd leading cancer killer in the United States among cancers that affect both men and women. It is estimated that 6 out of 10 (60%) deaths from colon cancer could be prevented if everyone were screened at 45.
Colon cancer is the 2nd leading cancer killer in the United States among cancers that affect both men and women. It is estimated that 6 out of 10 (60%) deaths from colon cancer could be prevented if everyone were screened at 45.
When detected early, colon cancer is up to 90% curable.
What are the risk factors?
It is important to know your risk, no matter how old you are. Some people may be at higher risk for the disease than others. You may be at higher risk if:
You are age 50 or older and
- You have a personal history of:
- Colon cancer
- Colon or rectal polyps
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis)
You have a family history of:
- Colon cancer
- Colon or rectal polyps
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
- Hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer
- Other cancers
Talk with your doctor about having earlier or more frequent tests if you think you are at higher risk for colon cancer. Talk with relatives about your family’s health history.
What are the symptoms?
Do not wait for symptoms to occur before getting screened. Early colon cancer often has no symptoms. If there are symptoms, they may include:
- Rectal bleeding
- Blood in the stool or in the toilet after having a bowel movement
- A change in your bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation
- Cramping or pain in the lower stomach
- Losing weight and you do not know why
- Anemia (low blood count)
- Learn More
Most colon cancer develops over time. A growth of abnormal tissue, called a polyp, forms on the lining of the colon. These usually start as non-cancerous (benign) polyps, but over time some change to be malignant, or cancerous. There are two types of polyps:
- Adenomatous polyps – polyps that can change into cancer, a pre-cancerous condition
- Hyperplastic polyps and inflammatory polyps – polyps that are non-cancerous
Many physicians believe that hyperplastic polyps could turn into pre-cancerous polyps or that those who have hyperplastic polyps have a greater risk of developing adenomatous polyps, especially when they are found in the ascending colon.
Other Colon Cancer Facts
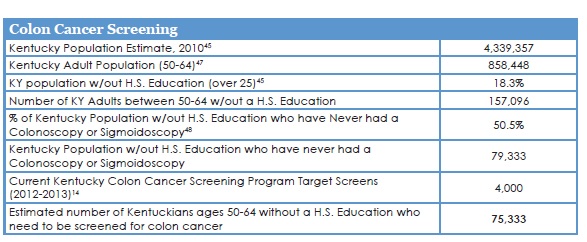
- Kentucky as of 2013 ranks No. 1 for colon cancer incidence and No. 4 for colon cancer mortality in the U.S.
- We can do something to change this.
You must be logged in to post a comment.